What is It and How Does a Projector Work?
By Phillip Park - 2024-8
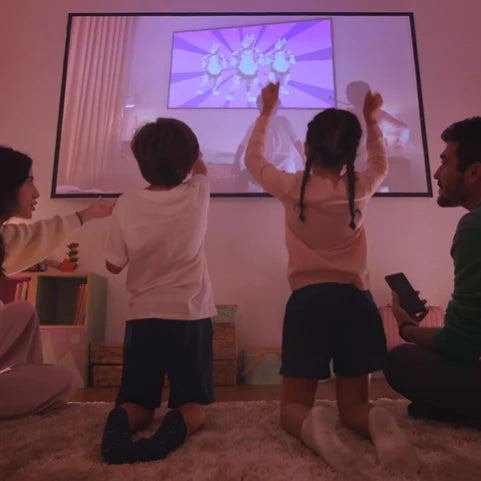
As a newly developed display device, projectors have swiftly gained popularity as a solution for commercial cinema in homes, schools, and offices. You've probably given buying one some attention if you're considering building your home theater room or remodeling your existing area. It is a wise decision since they have a great performance for viewing, cutting-edge technologies, and are highly compatible with various uses.
With so many different types of projectors available, it might be challenging to choose one that would work best for you. At the very beginning, let’s deal with the basic yet crucial questions of what it is and how a projector works.
What is a Projector and What Should You Know About It?
What does a projector mean? It usually refers to a digital modern device that you may use to put pictures, videos, files, or other types of material on a big surface or screen. It can be utilized in watching films and TV shows, giving speeches, teaching classes, presenting at conferences, and even singing Karaoke, etc. It functions by using light to project an image through a lens, which enlarges and concentrates the picture onto the appropriate surface, displaying the material in a bigger format.
Four Technical Specifications of Projectors You Should Know
You may get confused when looking at the spec table and don’t what they mean. Here are five main features that you may to be aware of to have a better understanding of projectors, which include the image resolution, color contrast, brightness, and throw ratio.
1. Image Resolution
Image resolutions stand for display clarity. Based on the number of pixels that may be shown on the screen, resolution dictates how clear the projected image will be. The common specifications for modern projectors are 720p, 1080p, and 4K. More pixels equal a higher resolution, which produces a picture that is sharper and more clear. Projecting complex charts, text, and high-definition movies requires this.
2. Color Contrast
Color contrast is one of the features that affect the picture quality. The difference in brightness between the image's white and black areas on the screen is known as the contrast ratio. You can notice more detail in the projected picture with a greater contrast ratio. A fuller image is produced by contrast, which also allows us to notice the nuances of color.
3. Brightness
Output
Generally speaking, a high-brightness projector will work best in rooms with greater natural light exposure if you desire brighter visuals. If you use it in a dark room, then it requires less brightness to see clear and rich-color images. Light source lumen, ISO lumen, and ANSI lumen are the units that describe the brightness output.
4. Throw Ratio
Throw ratio refers to the relation between the throw distance and the width of the projected image. The size of the image that a projector can produce at any given distance depends on its lens. Usually represented as a ratio, this is referred to as a "throw"; therefore, the name "throw ratio." Here’s the calculation formula: Throw Ratio = Throw Distance / Image Width
For example, if your projector has a throw ratio of 1.2 :1, it must be placed 120 inches distant from the screen to produce an image width of 100 inches.
How Does a Projector Work?
A projector receives and analyzes the visual signal when it is connected to a video source, such as a smartphone, computer, or other media player. The projector then produces a powerful beam of light by using a bulb or LED light source. This light is sent via several lenses and mirrors to assist focus and enlarge the picture. The audience may then view a bigger picture that has been projected onto a wall or screen thanks to the concentrated light.
Although there may be minor variations in the operation of various projector models, they always share the same fundamental idea and parts. To enlarge a display onto a projection screen, a projector essentially beams light through a digital picture, slide, film, or screen. Nearly every kind of projector has a few common components.
● First, the picture in front of the lens is reflected by mirrors in the majority of current projectors. However, depending on the kind, there might be significant differences in the types of mirrors and how they are employed.
● Every projector has a lens that enlarges the picture and controls how large a screen the image is projected onto. Projectors require a light source to shine onto mirrors or prisms, which then reflect the light through the lens and onto a projector screen to operate the lens.
● Lastly, the red, blue, and green, or RGB, light beam must be combined for digital projectors to show a color image. The most popular method for doing this is via a color wheel, however, chips may also be used to generate different hues, depending on the kind of projector.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does a Projector Work as a TV?
Present-day projectors are equipped with nearly every function seen on a television. We can watch live TV shows and sports games in the integrated Apps of the projectors, or connect it with a cable box or streaming devices like Roku, Apple TV, Fire Stick, and so on.
How Does a Projector Work with Phone?
One way is to connect your smartphone to the video projector via a HDMI cable or a USB Type-C cable. The other way is to wirelessly connect them by Bluetooth and WiFi-Cast/Screen Mirroring.
Conclusion
Projectors and TVs are now in competition in home theater setups because of features like HDR, 4K resolution, and fast refresh rates. However, because projectors are more flexible and portable than TVs, they provide you with greater freedom. Hope this guide can help you learn what it is and how a projector works in order to make an informed choice before buying.
Product Recommendations
Just Play,
Your Way

Mini Size, Maximum Entertainment

Mini Remote Control
Enjoy £10 off Your Next Purchase
Be the first to know about any news and sales!
*By subscribing, you agree to receive XGIMI's marketing emails and XGIMI's Privacy Policy.